Spring Framework의 특징
- 경량의 컨테이너로써 자바 객체를 직접관리 (메모리 관리관련)
- POJO(Plain Old Java Ojbect) 방식의 프레임워크
- IoC(Inersion of Control) 지원
- DI(Dependency Injection)지원
- AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming)지원
- iBatis, myBatis, Hibernate 등의 데이터베이스 라이브러리를 지원한다.
특징
- Java파일에서 Java 코드를 줄일 수 있다.
- 반복되는 작업을 줄일 수 있어 기능 개발에 집중할 수 있다.
- 프로젝트 관리가 용이하다.
- 다수의 개발자와 동시에 프로젝트 하기가 용이하다.
- 처음 프로젝트 셋팅이 다소 복잡하다.
- 개념을 제대로 숙지하지 못하면 코드 분석 조차 하기 힘들다.
스프링에서의 DI의 의미
- 부품들을 생성하고, 제품을 조립해주는 공정과정을 대신해 주는 라이브러리 (역할자)
* 개발 핵심 처리 루틴의 수정 없이 제품(객체)를 다른 제품(객체)로 쉽게 대체하여 생성 가능하도록 하는 역할을 함.
* 명세서에 따라서 자동적으로 부품을 활용하여 제품을 조립.
* 생성하기 원하는 객체를 명세서(XML)에 기술하고, 그 부품과 의존성(Dependency)들을 보관하는 일을 처리. 그러한 데이터를 보관하는 공간을 컨테이너라 함. (IoC 컨테이너)
2-4) XML (Bean) Sample
* 빈(Bean) 객체는 반드시 클래스를 사용. 인터페이스나 추상클래스는 객체 생성이 불가능함.
* 빈 객체 생성, 객체 초기화, 객체 값(또는 레퍼런스) 주입.
id : 빈 객체 고유 이름 (접근 가능자)
name : 객체의 이름(별칭)
class : 생성할 클래스
constructor-arg : 초기값 설정 (생성자 함수 사용) Java Class 에서
public Main(String name, String age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
property : 초기값 설정 (Setter함수 사용) Java Class 에서
public String name; setter, getter
<bean id=“빈 객체 고유 이름” name=“객체 이름” class=“생성할 클래스”>
<property name=“초기값 설정” value=“프로퍼티 값”></property>
</bean>
짧게 생략 가능 DI setter
<property name=“초기값 설정” value=“프로퍼티 값”></property>
<property name="height">
<value>프로퍼티 값</value>
</property>
DI 생성자
<bean id="빈 객체 고유 이름" class="생성할 클래스">
<constructor-arg value="생성자 첫번째" />
<constructor-arg value="생성자 두번째" />
<constructor-arg> // 3번째 생성자 ArrayList<String> 해당하는
<list>
<value생성자List[0]</value>
<value>생성자List[1]</value>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
줄여서 생략시 (c: constructor 줄임, p: property 줄임)
<bean id="빈 객체 고유 이름" class="생성할 클래스"
c:papaName="생성자첫번째" c:mamiName="생성자두번째" p:sisterName="프로퍼티 값">
<property name="초기값 설정" value="프로퍼티 값" />
</bean>
Java Bean 선언된 걸 xml에 선언된 Bean과 합치는 방법
package com.javalec.ex;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class ApplicationConfig {
@Bean
public Student student1(){
ArrayList<String> hobbys = new ArrayList<String>();
hobbys.add("수영");
hobbys.add("요리");
Student student = new Student("홍길동", 20, hobbys);
student.setHeight(180);
student.setWeight(80);
return student;
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd">
<context:annotation-config />
<bean class="com.javalec.ex.ApplicationConfig" />
<bean id="student2" class="com.javalec.ex.Student">
<constructor-arg value="홍길순"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="30"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg >
<list>
<value>마라톤</value>
<value>요리</value>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
<property name="height" value="190" />
<property name="weight" value="70" />
</bean>
</beans>
package com.javalec.ex;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private ArrayList<String> hobbys;
private double height;
private double weight;
public Student(String name, int age, ArrayList<String> hobbys) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.hobbys = hobbys;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setHobbys(ArrayList<String> hobbys) {
this.hobbys = hobbys;
}
public void setHeight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
public void setWeight(double weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public ArrayList<String> getHobbys() {
return hobbys;
}
public double getHeight() {
return height;
}
public double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
}
package com.javalec.ex;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationCTX.xml");
Student student1 = ctx.getBean("student1", Student.class);
System.out.println("이름 : " + student1.getName());
System.out.println("나이 : " + student1.getAge());
System.out.println("취미 : " + student1.getHobbys());
System.out.println("키 : " + student1.getHeight());
System.out.println("몸무게 : " + student1.getWeight());
Student student2 = ctx.getBean("student2", Student.class);
System.out.println("이름 : " + student2.getName());
System.out.println("나이 : " + student2.getAge());
System.out.println("취미 : " + student2.getHobbys());
System.out.println("키 : " + student2.getHeight());
System.out.println("몸무게 : " + student2.getWeight());
ctx.close();
}
}
xml Bean 선언된 걸 Java에 선언된 Bean과 합치는 방법
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="student2" class="com.javalec.ex.Student">
<constructor-arg value="홍길순"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="30"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg >
<list>
<value>마라톤</value>
<value>요리</value>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
<property name="height" value="190" />
<property name="weight" value="70" />
</bean>
</beans>
package com.javalec.ex;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportResource;
@Configuration
@ImportResource("classpath:applicationCTX.xml")
public class ApplicationConfig {
@Bean
public Student student1(){
ArrayList<String> hobbys = new ArrayList<String>();
hobbys.add("수영");
hobbys.add("요리");
Student student = new Student("홍길동", 20, hobbys);
student.setHeight(180);
student.setWeight(80);
return student;
}
}
package com.javalec.ex;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private ArrayList<String> hobbys;
private double height;
private double weight;
public Student(String name, int age, ArrayList<String> hobbys) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.hobbys = hobbys;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setHobbys(ArrayList<String> hobbys) {
this.hobbys = hobbys;
}
public void setHeight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
public void setWeight(double weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public ArrayList<String> getHobbys() {
return hobbys;
}
public double getHeight() {
return height;
}
public double getWeight() {
return weight;
}
}
package com.javalec.ex;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ApplicationConfig.class);
Student student1 = ctx.getBean("student1", Student.class);
System.out.println("이름 : " + student1.getName());
System.out.println("나이 : " + student1.getAge());
System.out.println("취미 : " + student1.getHobbys());
System.out.println("키 : " + student1.getHeight());
System.out.println("몸무게 : " + student1.getWeight());
Student student2 = ctx.getBean("student2", Student.class);
System.out.println("이름 : " + student2.getName());
System.out.println("나이 : " + student2.getAge());
System.out.println("취미 : " + student2.getHobbys());
System.out.println("키 : " + student2.getHeight());
System.out.println("몸무게 : " + student2.getWeight());
ctx.close();
}
}
스프링 빈 생명주기
인터페이스 이용시

어노테이션 이용시

스프링 빈 범위(scope)

scope default 는 singleton이다.
properties 외부파일 사용
오라클 경우
context.xml 파일설정
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:config/properties/db.properties"/>
<!-- bean id="dataSourceProxy" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"-->
<bean id="dataSourceProxy" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${db.driverClassName}"/>
<property name="url" value="${db.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${db.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${db.password}" />
</bean>db.properties 설정
db.driverClassName=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
db.url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@오라클주소이름 ex)localhost:1521:aaa or www.xxxx.xxx:1521:aaa
db.username=아이디 (오라클 아이디)
db.password=패스워드 (오라클 비밀번호)
MySql 경우
context.xml 파일설정
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:config/properties/db.properties"/>
<!-- bean id="dataSourceProxy" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"-->
<bean id="dataSourceProxy" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${db.driverClassName}"/>
<property name="url" value="${db.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${db.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${db.password}" />
</bean>db.properties 설정
db.driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
db.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/aaa?
useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&verifyServerCertificate=false&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
db.username=아이디 (mysql 아이디)
db.password=패스워드 (mysql 비밀번호)
2. 능동 변환 : SpEL
두 번째는 SpEL(Spring Expression Language)를 이용하는 방법이다.
빈 팩토리 후처리기에서 치환을 해주는 수동적인 방법과 달리, 빈 오브젝트에 직접 접근할 수 있는 표현식을 이용해 원하는 프로퍼티 값을 능동적으로 가져오는 방법이다. (스프링 3.0 에서 소개됨)
SpEL은 다른 빈의 프로퍼티에 접근, 메소드 호출, 다양한 연산도 지원하며 클래스 정보에도 접근할 수 있다. (생성자를 호출해서 오브젝트를 만들 수도 있음)
<util:properties> 태그를 이용하면 프로퍼티 파일을 읽어서 Properties 타입의 빈으로 만들 수 있다.
<util:properties id="database" location="classpath:database.properties"/><context:property-placeholder> 처럼 빈 팩토리 후처리기로 동작해서 빈의 값을 변경하는 것이 아니라, 단순히 프로퍼티 파일의 내용을 담은 Properties 타입의 빈을 만들어 준다.
이렇게 database.properties의 내용을 빈으로 만들어두고, dataSource 빈에서는 SpEL을 이용해서 database 빈 오브젝트에서 원하는 정보를 읽어오게 한다. (SpEL에서는 Map의 get() 메소드를 호출해주는 표현식이 존재하는데, []안에 키 값을 넣어주면 된다.)
<bean id="dataSource" class="..DataSource">
<!-- database 빈 오브젝트에서 db.driverclass를 키로 갖는 값을 가져오라는 표현식 -->
<property name="driverClass" value="#{database['db.driverclass']}"/>
...
</bean>@Value("#{database['db.driverClass']}") 로도 가능하다.

AOP

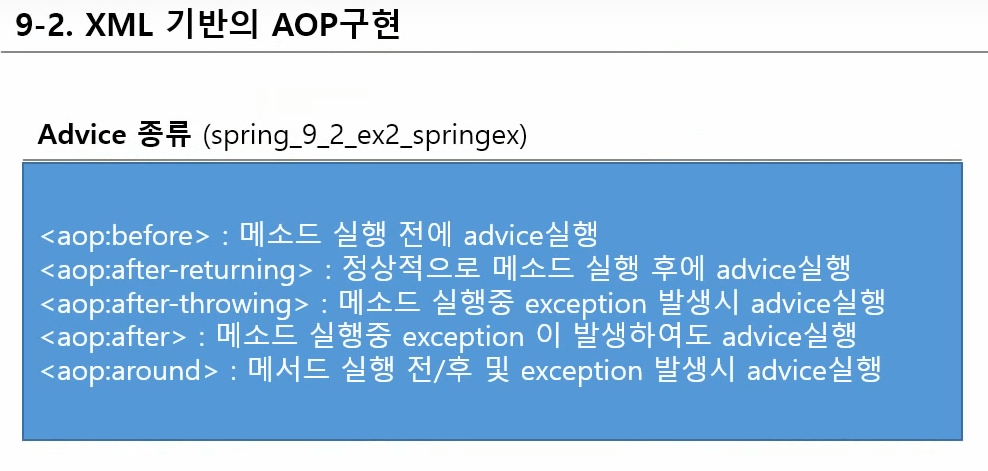
<bean id="logAop" class="com.javalec.ex.LogAop" />
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="logger" ref="logAop">
<aop:pointcut id="publicM" expression="within(com.javalec.ex.*)" />
<aop:around pointcut-ref="publicM" method="loggerAop" />
</aop:aspect>
<aop:aspect id="logger" ref="logAop">
<aop:pointcut id="publicM" expression="within(com.javalec.ex.*)" />
<aop:before pointcut-ref="publicM" method="beforeAdvice" />
</aop:aspect>
<aop:aspect id="logger" ref="logAop">
<aop:pointcut id="publicM" expression="within(com.javalec.ex.*)" />
<aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="publicM" method="afterReturningAdvice" />
</aop:aspect>
<aop:aspect id="logger" ref="logAop">
<aop:pointcut id="publicM" expression="within(com.javalec.ex.*)" />
<aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="publicM" method="afterThrowingAdvice" />
</aop:aspect>
<aop:aspect id="logger" ref="logAop">
<aop:pointcut id="publicM" expression="within(com.javalec.ex.*)" />
<aop:after pointcut-ref="publicM" method="afterAdvice" />
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>

'Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 인터셉터 HandlerInterceptorAdapter 제공 메소드 (0) | 2020.12.18 |
|---|---|
| 이클립스 Spring STS 수동설치 (0) | 2020.12.15 |